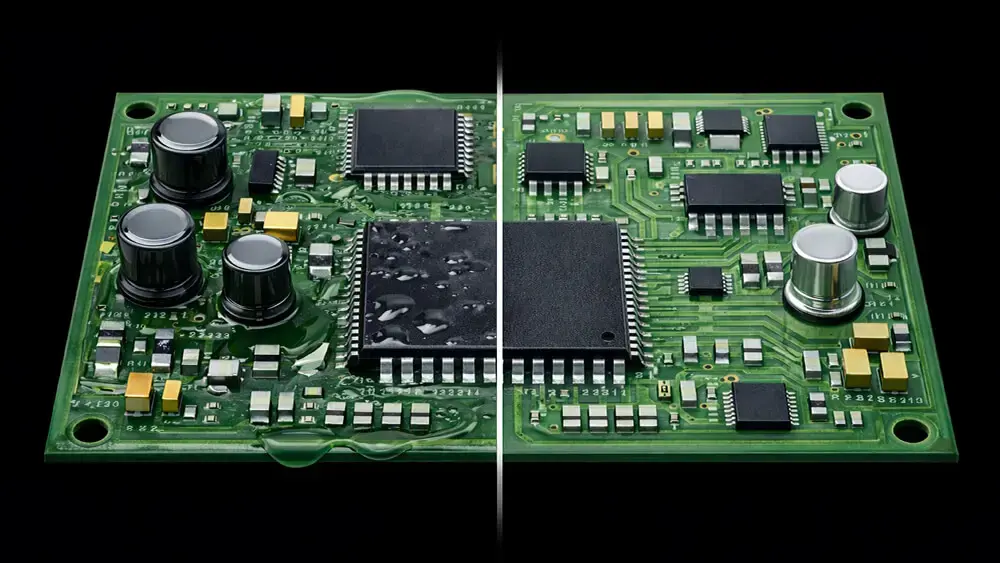
A side-by-side comparison of three thin film coating technologies for electronic applications.
R&D product leaders like you and me drive innovation. We turn ideas and problems into safe and manufacturable products by exploring new technologies, materials, and processes to meet technical needs and customer expectations. One such need and expectation is the development of smaller, "smarter," more reliable components and products.
Protective coatings, particularly thin films (materials with thicknesses ranging from a few nanometers to a few micrometers), are one way to enable this development. Three of these coating techniques are thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), and Plasma-enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD). Each of these techniques can deposit a wide range of materials.
Read more about HZO Guardian Plus Parylene Coatings
Let's examine the basic science behind each coating and the pros and cons of each. By the end of this overview, you should have a good idea of which option might be best for you, but I'll sum things up with some generalizations and questions you and your team can ask as you continue your research. This won’t be as much of a scientific paper, but rather a plain-language or conversational explanation of the concepts. If you’d like a deeper dive into the science, feel free to contact me personally and set up a meeting.
What Makes a Good Protective Coating?
But before I dive in, let's align on what aspects of the coating you will likely be interested in. I realize everyone's knowledge of thin film coatings may vary. My company has a resource page, and I also recommend this paper by Vasilyev here to explore the science of thin film coatings further. However, in general, depending on your product, you might prioritize understanding the following:
Conformality: Can the coating reach deep crevices and cover 3D geometries evenly?
Barrier Properties: How well does it block moisture, oxygen, or gases?
Mechanical Properties: Will it withstand abrasion or flexing?
Dielectric Performance: Is it insulating enough for sensitive or higher-power electronics?
UV Resistance: Will it hold up in direct sunlight or sterilization conditions?
Process Constraints: These include throughput, masking needs, temperature, etc.
With those criteria in mind, let's look at Parylene, ALD, and PECVD coatings. For transparency, these are the coatings we offer or have offered at my company, HZO, which is also why I can speak to the science. I optimize and solve problems with these materials and processes every day.
Parylene: Flexible, Reliable, Conformal, Thicker
Parylene is a vapor-deposited polymer known for uniformly coating complex shapes and internal crevices. This is thanks to its long-lived reactive species, which can travel deep into structures before reacting.
Parylene is deposited using a thermal chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process, which means it has a better “throw,” allowing you to get really conformal around components. The thermal activation of the precursor molecules typically allows the activation to last longer than an electrical activation. Parylene would be able to get inside smaller or deeper crevices, and you'd be able to coat hidden and difficult-to-reach areas that you normally can't conformally coat in a dip coating process.
The coating is also flexible, but thick. And by thick - I mean relatively thick. Compared to an acrylic conformal coating, Parylene coatings are typically half as thick. But we're comparing it to the coatings yielded by the other two techniques in this overview - PECVD and ALD.
A common Parylene coating project is 7-25 microns thick. PECVD coatings could be 6 microns thick, but they are routinely 0.8-2.7 microns thick, and ALD coatings get even thinner. This is typical, but at HZO, we do a lot of customization, so if you have a question about a different thickness, please reach out.

A low magnification SEM image (left) and a corresponding Cl (chlorine) map (right) of a cross-section of a board-to-board connector. Note that the 10-micron thick coating covers the surfaces of the thin gap under the connector, reaching as far as the edge of the opening allowed it to.
If you need to coat underneath pins or if you need to coat in some crevices, then Parylene's a good balance between having something that's really conformal and not too thin versus something that's not conformal enough. I'll sum up Parylene's strengths and limitations below.Strengths:
- Excellent conformality, ideal for intricate 3D designs
- Thick, flexible, and durable: its polymer backbone offers a good mix of pliability and robustness
- Strong dielectric performance: effective at blocking electron flow
- Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR) is competitive at thicker layers
Limitations:
- Soft surface: can be prone to scratching
- UV degradation: prolonged UV exposure can lead to performance breakdown over time
ALD Coatings: Thinnest, Most Conformal, Superior Barrier Properties

Snapshot of the ALD Process.
Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) is a nanotechnology workhorse that builds coatings one atomic layer at a time in a coating chamber, similar to CVD. The result is an ultra-thin, pristine, and incredibly conformal film with unmatched barrier properties.ALD is highly regarded for conformal coverage; it’s a lot more conformal than the CVD process used with Parylene. It is particularly suited for high aspect ratio structures because it can form a coating wherever the gas absorbs onto a surface. This gas is an unactivated gas or said another way, the gas is not in an excited state, instead it has a high chemical potential. When you send in the second gas, the second gas reacts with the first gas to make a film or an atomic layer coating. You can get this coating inside of many crevices, corners, and high-surface-area things, since anywhere both gases touch the surface, there could be a deposition. In contrast, Parylene has a limited number of times it can bounce off of a wall before it reacts and deposits on the wall. A problem with the ALD technique is that it takes a lot longer to deposit because the coating is built one layer at a time. If you want to build up a lot of layers, that takes a lot of time, which will be more costly. The layers that are deposited with ALD are normally of a ceramic nature including layers composed of alumina, titania, or silica, all of which are hard and brittle materials. Since the coatings are layered out atomically, there are less defects in the layers and that's great for protection because you could have a good barrier without any holes or gaps. Problems do arise because the ALD coatings are so thin and brittle, they can easily be broken or fractured. So, if you keep the ALD coating intact by making them the correct thickness, or adding other material layers, then it'll shield your products from many harmful gases, liquids, and harsh environments with very little thickness.Usually, when you have an ALD process, you want to layer the coating. The coatings are layered with some other material that is deposited at a much faster rate, such as adding a CVD or PECVD layer that'll help protect the ALD layer, add flexibility, and add capabilities that outperform CVD and PECVD coatings alone. ALD is better at blocking gases. For example, if you want no oxygen, water, water vapor, or any kind of gas to pass through, then ALD would help you do that with a really thin layer.Here are some strengths and limitations of Atomic Layer Deposition coatings.Strengths:
- The best conformality of the three processes, even in ultra-high aspect ratio features
- Pristine chemical layer with very little defects: excellent for gas and moisture barriers
- Extremely thin coatings: great when size and weight matter
Limitations:
- Slow deposition process: less ideal for high-throughput production
- Fragile: typically, a ceramic film is best used as part of a multi-layer stack to prevent defect formation and cracking
PECVD: Fast, Versatile, and UV-Resistant

Snapshot of the PECVD Process.
Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a plasma-assisted deposition technique that offers flexibility and speed. PECVD applied coatings excel in applications requiring thinner coatings (<6 microns) and at these thinner coating levels they give better protection than the equivalent thickness of a parylene coating. They can be hydrophobic, more oleophobic, transparent to high frequencies, and UV resistant.
Have more questions about the different properties of PECVD coatings? Contact me.
PECVD-applied coatings can be deposited quickly and made in layers. For example, you can have a hard layer that is less conformal and more of a line-of-sight coating, and you could include that with a more conformal layer that is softer, but penetrates deeper into crevices. Then, the last or top layer could be a highly hydrophobic layer to prevent liquid water from ingressing into the stack or it could be harder layer to prevent the stack from being scratched.
PECVD coatings are a lot more conformal than many other coating techniques, but out of the three coatings we are discussing here, the PECVD coatings are less conformal because you have to activate your species electrically in a plasma, and that activated chemical has a limited lifetime.
In other words, if the travel time required before your activated gas reacts with a surface is too great because the area to coat is too far away or around too many corners, then that area will get less to no coating. The activated species has a limited time remaining active once it leaves the plasma zone.
PECVD coatings are often chosen for their hydrophobic properties and UV resistance, which are crucial in specific applications. Take hydrophobicity. Water carries ions, and those ions help transport electricity and water itself. All devices run on some kind of electricity. So we want to prevent the water from staying on the board and causing damage from the ions. The hydrophobicity prevents the water from staying on the board if the board isn’t immersed in water.
Think about the typical use case for electronic devices—most entail only temporary exposure to water. Even though our PECVD coatings can be tailored for longer exposure to water, sweat, or other harmful solutions in tests such as the IPX7 or IPX8 tests, all of our PECVD coatings are significantly hydrophobic regardless of thickness. For example, we will probably spill water on our laptop; we won't use it underneath a pool. Hydrophobicity helps a lot with that. If the water gets into a little crack, capillary forces keep it in. If everything is hydrophilic, the water will want to stay in these cracks.
Of course, this causes problems you may not see with your computer right after the spill, but later on, corrosion develops because the water is still stuck in there.
Hydrophobicity helps the water not want to be there anymore. It pushes it out and helps it evaporate quickly, preventing the water from sitting on your device for too long. Meanwhile, UV resistance is critical for any application outside and not already in some kind of housing. Other coatings will degrade and break down in UV exposure, and so will their protection. This isn't the case with PECVD coatings.
A huge benefit of going with a thinner PECVD coating is the potential for cost savings. Six microns or less is generally the cut-off for costs. If you can keep close to this thickness layer, you can have punch-through capabilities. This means that when you have a connection that's often removed and put back on, you're punching through the coating once you plug in that connection.
It is true that if you remove that connection from where it was plugged in, it isn't protected anymore. But other products like greases can help protect that area from water ingress, so if you want to plug in and unplug something while it's underwater, then greasing up that connection will help a lot, but as mentioned above a product with a thin plasma coating wouldn’t be constantly used in an underwater environment.
This will drastically reduce or eliminate the need for masking parts, reducing the price of the coating process and the cost of repairing it. If you need some areas without coating, you can use shadow masking, which is much cheaper than actual masking with glues.
Another benefit of the thin PECVD coatings is their ability to be transparent for high-frequency signals like radio waves, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or other signals that your device will be sending or receiving. One reason for this is the thin nature of the PECVD coatings, and the other is the low loss tangent of the chemistry.
Strengths:
- Better for thinner coatings with high hydrophobicity
- UV resistance: performs well in sunlight or sterilization environments
- Shadow mask & punch-through capable: supports selective patterning
- Faster processing, particularly for high-volume needs
- Flexibility with layered chemistries beyond our standard coatings
- Transparent to higher frequency signals
Limitations:
- Softer than Parylene, offering less abrasion resistance
- Extended immersion protection requires thicker films
- Part size height limitations due to electrode-based chambers
Masking & Process ConsiderationsMasking can make or break your process regarding costs, especially when integrating coatings into production. The more your part is handled, and the more time is spent with it, the more costly the process could become. Here's how each technology compares:
- Parylene: Complex to mask, but excellent for full encapsulation >6µm thick
- ALD: Higher masking complexity. Best conformality of the three.
- PECVD: Compatible with shadow masks and patterning
Comparison Table: Quick Reference
| Feature |
Parylene |
ALD Coatings |
PECVD Coatings |
| Conformality |
High |
Highest |
Moderate
|
| Dielectric Properties |
Excellent |
Moderate |
Good
|
| Mechanical Properties |
Flexible, relatively thick |
Fragile (ceramic) |
Softer than Parylene |
| WVTR/Barrier Performance |
Good, relatively thick |
Excellent, thin |
Moderate |
| UV Resistance |
Low |
Moderate |
High |
| Hydrophobicity |
Moderate |
Low |
High |
| Process Speed |
Moderate |
Slow |
Fast |
| Masking Complexity |
High |
High |
Moderate-Low |
| Coating Cost (Speed+Masking) |
Moderate |
High |
Low-Moderate |
| Best Use Case |
Flexible, dielectric |
Ultra-thin, barrier |
UV, incidental |
How to Choose the Right Coating: A Guide for R&D Engineers

What are the common factors influencing the choice of one coating technology over another?
Factors to think about are what environment your end product is going to be in and what the coating will cost. Do you have something that's going to be underwater all the time and can cost more? Parylene is your best bet. Do you need to ensure that there's no particular ingress of a certain gas species in your environment? You might need an ALD coating to help with the protection you need. And if you need this to be out in a UV environment where we don't want any of it to degrade, then a plasma coating is a better choice. Do you just need to extend the life of your product by keeping water and sweat away? Then, a hydrophobic PECVD coating would work great.
Another factor is longevity. Do you want your product to last for years? Tens of years? Hundreds? We know that the longer you want a coating and its protection and enhancement to last, usually, the bigger, the thicker, and the more durable the coating needs to be. Most of our plasma coatings are thinner and help you protect a product from incidentals, but not for continuous immersion uses, although mass production coatings with a harder outer layer are being developed.
Ultimately, though, I'm afraid there's no "winning" coating here. Only the right tool for the job. Some good questions to ask as you continue your research might be:
- What are you protecting against? (moisture, UV, abrasion?)
- What is the geometry of your part?
- Are dielectric properties critical?
- What's your target thickness, cost, and scalability?
- Does your design require masking or selective coverage?
And some general advice?
- Choose Parylene when flexibility and conformality are essential.
- Use ALD when you need ultra-thin, ultra-pure, and gas-impermeable films.
- Go with PECVD when UV exposure, hydrophobicity, or transparency to high frequencies are requirements, and cost is a concern.
Final Thoughts: Match the Coating to the Mission
As electronic products evolve, so do the challenges we face in protecting them. At the R&D level, your coating decision shapes product performance, manufacturability, and regulatory compliance.
If you're unsure which path to take, consider running early coating tests with your development partner. We have found that in some situations, a hybrid or stacked solution (combining strengths from multiple technologies) yields the best results.
Want help evaluating coatings for your next product? Are you facing a problem with your current solution and starting to feel like you need an unprecedented solution? Let's talk. Use the contact us form to message me, and I will reply. I'm happy to share more about what I know to help you solve a problem, innovate a solution, or develop new technology.