Tensile Strength at Yield - Testing, Standards, Specs, Material

The ability to accurately predict the behavior of coating materials under tension is crucial in ensuring the integrity and reliability of electronic components. This includes studying different materials' deformation and failure mechanisms when subjected to a tensile load. One key parameter that is used to quantify the ability of a material to withstand such loads is its tensile strength at yield.
What is Tensile Strength at Yield?
Tensile Strength at Yield indicates a material's ability to withstand loads and forces during its lifetime, making it crucial for designing structures and components that can endure various stresses. It is a vital measurement in numerous disciplines, such as engineering, manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive.
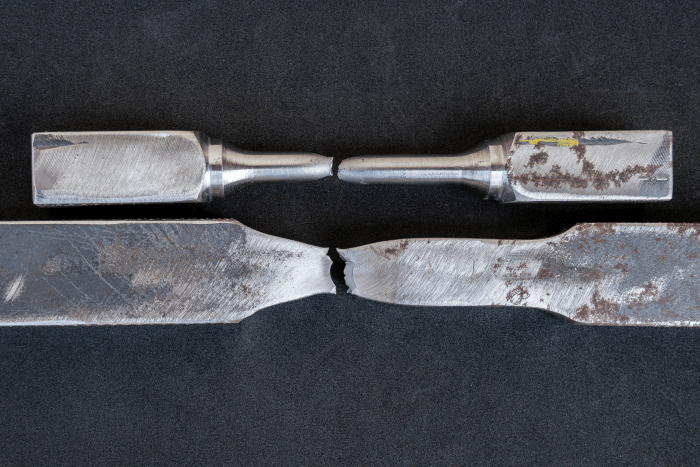
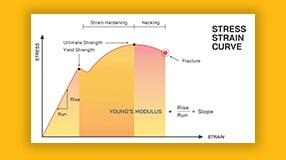
When a material is subjected to a tensile load, it experiences stress and undergoes deformation. The stress-strain curve, representing the relationship between the applied stress and resulting strain, provides valuable insights into the material's behavior. This curve can determine the ultimate tensile strength, the maximum stress the material can withstand before failure occurs.
The yield point is a critical parameter in studying tensile strength at yield. It refers to the point on the stress-strain curve where a significant increase in strain occurs with minimal or no increase in stress. The tensile strength at yield is the stress level at this point and represents the maximum stress a material can withstand without undergoing permanent deformation.
During the deformation process, materials can exhibit different types of behavior. Elastic deformation occurs when a material returns to its original shape upon removal of the load, while plastic deformation occurs when the material undergoes permanent changes in shape. Understanding the concepts of elastic and plastic deformation is essential in analyzing a material's behavior under tension.
Testing Methods, Equipment, and Standards Used for Measurement
Due to the importance of this mechanical material property, obtaining accurate Tensile Strength at Yield data is critical. Accurately measuring it requires appropriate testing methods, equipment, and adherence to specific standards. The most commonly used technique is the tensile test, where a sample material is subjected to an increasing axial load until it reaches its yield point. Sophisticated equipment, such as universal testing machines, performs these tests and obtains reliable measurements. Standard organizations, such as ASTM International, provide guidelines and standards for conducting these tests, ensuring consistency and comparability of results.
Standards and Specifications
Standards and specifications are crucial in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of measurements. National and international organizations have established various standards to regulate this critical characteristic of materials.
Similarly, numerous national and international standards have been developed to guide the measurement and characterization of tensile strength at yield. These standards outline the specific testing methods, equipment, and conditions to ensure accurate and comparable results across different laboratories and industries.
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) are among the leading organizations that have established widely recognized standards for tensile strength at yield. Compliance with these standards is essential in ensuring test data's uniformity, reliability, and compatibility.
What Influences Tensile Strength at Yield?
Material composition plays a crucial role in determining values. Different elements and their proportions can significantly affect the mechanical properties of a material, including its yield strength. For example, increasing the amount of carbon in certain materials can enhance tensile strength at yield.
The microstructure of a material also plays a vital role in determining this value. Factors such as grain size, phase distribution, and dislocation density can impact the material's ability to withstand deformation before yielding.
Coating Material Selection and Design Factors
Because this mechanical property is crucial in determining various structures and products' overall reliability and safety, it should be closely considered during material selection. Every industry and application has unique requirements for choosing a coating material. Engineers must account for environmental conditions, load-bearing capacity, and durability requirements. They can select appropriate materials to meet the desired performance and safety standards by evaluating the tensile strength at yield requirements specific to each industry. A summary of requirements for particular applications is below.
Evaluating Tensile Strength at Yield requirements for different industries
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, where extreme conditions and rigorous performance requirements exist, coating materials with exceptional tensile strength at yield are crucial. This property ensures aircraft components' structural integrity and safety, such as wings and fuselage, under immense stress during flight.
- Automotive: This property is vital in automotive engineering as it affects vehicle structural stability. Manufacturers and designers prioritize coating materials with optimal values to enhance passenger safety and overall vehicle performance.
- Consumer products: From household appliances to sports equipment, consumer products are designed to withstand daily usage and potential impacts. Tensile strength at yield is vital in ensuring that these products can withstand the forces they are subjected to without deforming or failing.
Importance in Coating Material Selection
Tensile strength at yield is a critical mechanical property used in coating material selection. It provides valuable information about the protective coating material's ability to withstand applied forces without permanent deformation. If a protective coating were to break, it could allow corrosives and contaminants to destroy electronic components, causing failure.
Design engineers rely on this property to evaluate and compare different coating materials, ensuring their suitability for specific applications. If you are designing an electronic component and need help determining which coating material is best for your product, please contact our engineers, or read additional information on thin film coating properties.
UL94 Coating Material - Testing Method, Material Selection
What is Dielectric Strength? Formula, Testing, Table of Values
Elongation Yield: Overview, Unit of Measure, Data and Testing
Mallory is a veteran writer with over a decade of writing experience and has spent over five years at HZO learning about coating technology from the best minds in the industry. Professionally, Mallory is especially interested in the process of problem-solving and watching how the engineering team develops solutions that ensure business requirements are met. Over her years at HZO, Mallory's writing has been cited in industry whitepapers, including "Parabolic Model for Optimum Dry Film Thickness (DFT) of Corrosion Protective Coatings" and "Universal Approach to Integrating Reduced Graphene Oxide into Polymer Electronics." All of Mallory’s blogs are reviewed for accuracy before publication.
Additional Resources

Understand the Capabilities of Thin Film Coatings With Our Resource Page

Understand UL94 Rating - Testing, How to Choose a Material, and More

What's the Difference Between Hydrophobic Coatings and Hydrophilic Coatings?

Dielectric Constant of Insulator - Materials, Formula, Table of Values

Tensile Strength at Yield - Testing, Definition, Material Selection
Young's Modulus of Polymers - Measurement, Calculation, Material Selection

Volume Resistivity - Definition, Measurement, Implications For Product Design

Polymer Glass Transition Temperature – Material Properties, Impact

What is Coefficient of Linear Expansion? Formula, Units & More

Learn About the Thin Film Coating Properties and Processes In Our Webinar

The Difference Between "Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic" Coating Properties

Learn about Protective Coating Methodologies With Our White Paper