Epoxy Conformal Coating Evaluation Guide

Conformal coatings are polymeric materials applied to substrates. These films protect electronics from environmental hazards, like corrosion, humidity, chemicals, and liquids. Popular conformal coating materials include silicone, acrylic, Parylene, and urethane. Epoxy is a top coating for applications that need high chemical and abrasion resistance.
What is Epoxy Conformal Coating?
Epoxy coatings are protective layers of polymeric material. They have excellent electrical, thermal, mechanical, and moisture barrier properties.
Epoxy coatings have the following attributes:
- Very robust; difficult to remove the protective coating.
- Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance
-
Very rigid conformal coating.
-
High dielectric strength
Epoxy Conformal Coating Applications
Epoxies are tough and highly abrasion-resistant. So, they are common in harsh environments, like automotive, marine, and military applications.
While exact figures for epoxy coatings specifically are not provided, the overall conformal coatings market is projected to see strong growth:
The global conformal coatings market is expected to reach $1.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 5.3%. Some estimates project the market to reach $2.11 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 6.7%.
Epoxy conformal coatings find use in various industries and applications:
• Consumer electronics
• Automotive electronics
• Aerospace and defense
• Industrial equipment
• Medical devices
They are particularly suitable for applications requiring rigid, durable coatings with good chemical and abrasion resistance.
Different types of epoxies have other benefits. For example, thermally conductive epoxy can protect boards with hot components. Meanwhile, flame-retardant epoxy protects against fire hazards. Clear epoxy allows for board visualization.
HZO provides Parylene conformal coatings applied with vacuum deposition, so our process is different. Watch this video to learn more.
What Does Epoxy Conformal Coating Protect Against?
Epoxy conformal coatings resist chemicals, alkalis, acids, moisture, solvents, and salt spray. They are known for excellent adhesion to various substrates without primers. They also retain this adhesion under many conditions. Additionally, they have good electrical properties. These remain stable despite humidity or high temperatures.
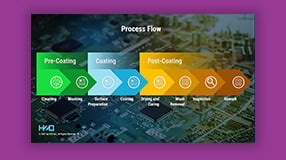
The Epoxy Conformal Coating Process
Applying epoxies with dip coating, brush, or spray application techniques is easy. Dip coating involves immersing a component in a tank of coating material. Brushing entails a manual application by an operator. The spraying method can be automated or manual, depending on production needs. Epoxy materials are a single or two-part compound. They require curing with UV or heat.
Learn About Conformal Coating vs. Potting
Epoxy Conformal Coating Pros and Cons
Advantages
- Good abrasion resistance.
- Good chemical resistance.
- High tensile strength.
- High Youngs Modulus.
- Low coefficient of linear expansion.
Disadvantages
- Higher water absorption than Parylene.
- Rigid, can crack in vibration or thermal cycling.
- Can shrink, causing stress on components/diodes.
- Very difficult to rework.
- Low impact resistance.
- Low abrasion resistance compared to Parylene.
Why Choose Epoxy Conformal Coating to Protect Your Electronic Devices?
Epoxies have strong barrier properties; they are easy to process and cheap. That said, epoxy coating's toughness may complicate rework and removal. Film shrinkage may occur during polymerization, causing issues. The suggested thickness for epoxy coatings can reach 130 micrometers. This thickness may prove too bulky for applications that entail miniaturization.
Need help choosing a coating material for your next project? Contact us to discuss your application with a coating expert.
Conformal Coating Removal - How to Get Started W/Reference
Polyurethane Conformal Coatings - Benefits & Applications
6 Common Conformal Coating Defects & Their Solutions
Mallory is a veteran writer with over a decade of writing experience and has spent over five years at HZO learning about coating technology from the best minds in the industry. Professionally, Mallory is especially interested in the process of problem-solving and watching how the engineering team develops solutions that ensure business requirements are met. Over her years at HZO, Mallory's writing has been cited in industry whitepapers, including "Parabolic Model for Optimum Dry Film Thickness (DFT) of Corrosion Protective Coatings" and "Universal Approach to Integrating Reduced Graphene Oxide into Polymer Electronics." All of Mallory’s blogs are reviewed for accuracy before publication.
Additional Resources

Which is Better For Your Application? Conformal Coating or Potting?

Learn About Common Conformal Coating Defects And How To Fix Them
Learn How To Incorporate Conformal Coating Into Your Manufacturing Process









